A wide range of products that are used daily by consumers and industries worldwide incorporate Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) because of its versatile characteristics. One particularly beneficial property of PVC is its waterproof nature, making it a preferred choice in marine applications. The seam bond in PVC products, as a result, needs to be extremely durable to resist the demanding conditions, and the type of welding method used can significantly influence this bond strength.
In this article, we will delve into the world of PVC welding, discussing various types of welding methods and how they impact the final product. By understanding these distinctions, small to medium-sized manufacturers can optimize their production processes and generate products of superior quality and resilience.
For more articles about PVC welding click here
Understanding PVC Welding
PVC welding, while a relatively technical term, is central to manufacturing processes involving thermoplastic materials. Simply put, PVC welding is a method used to join two pieces of PVC materials together. This process harnesses the application of heat to the contact points between materials, leading to a fusion that forms a strong bond.
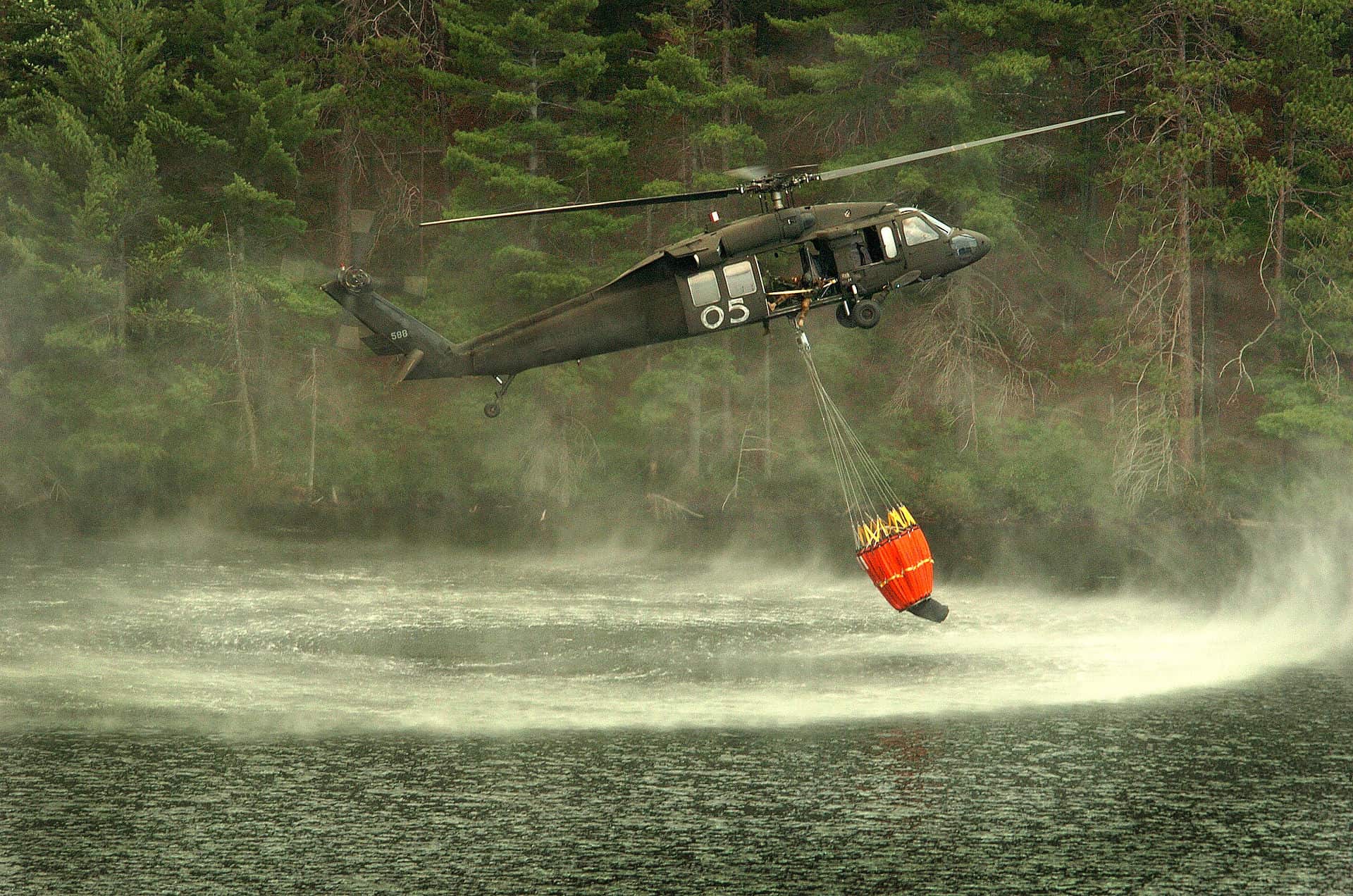
Why is PVC welding necessary, you ask? Consider the structure and needs of a waterproof boat cover or an inflatable water raft. These products should not only resist water penetration but also withstand the dynamic stresses of use. The strength of the seam bond created by PVC welding is what provides these essential qualities.
Across different industries, PVC welding has gained a reputation for delivering durable products. From construction to automotive and marine applications, the range is extensive and the importance of this technique can barely be overstated.
Understanding PVC welding ensures durability and resilience in the face of wear and tear and provides the potential for architecting complex designs without compromising structural integrity.
The key to Successful PVC welding
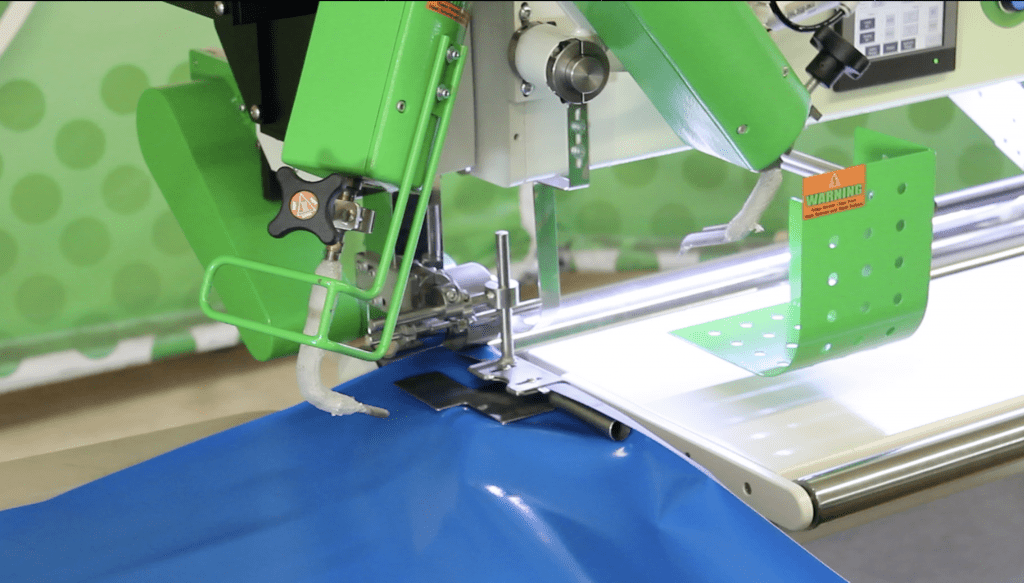
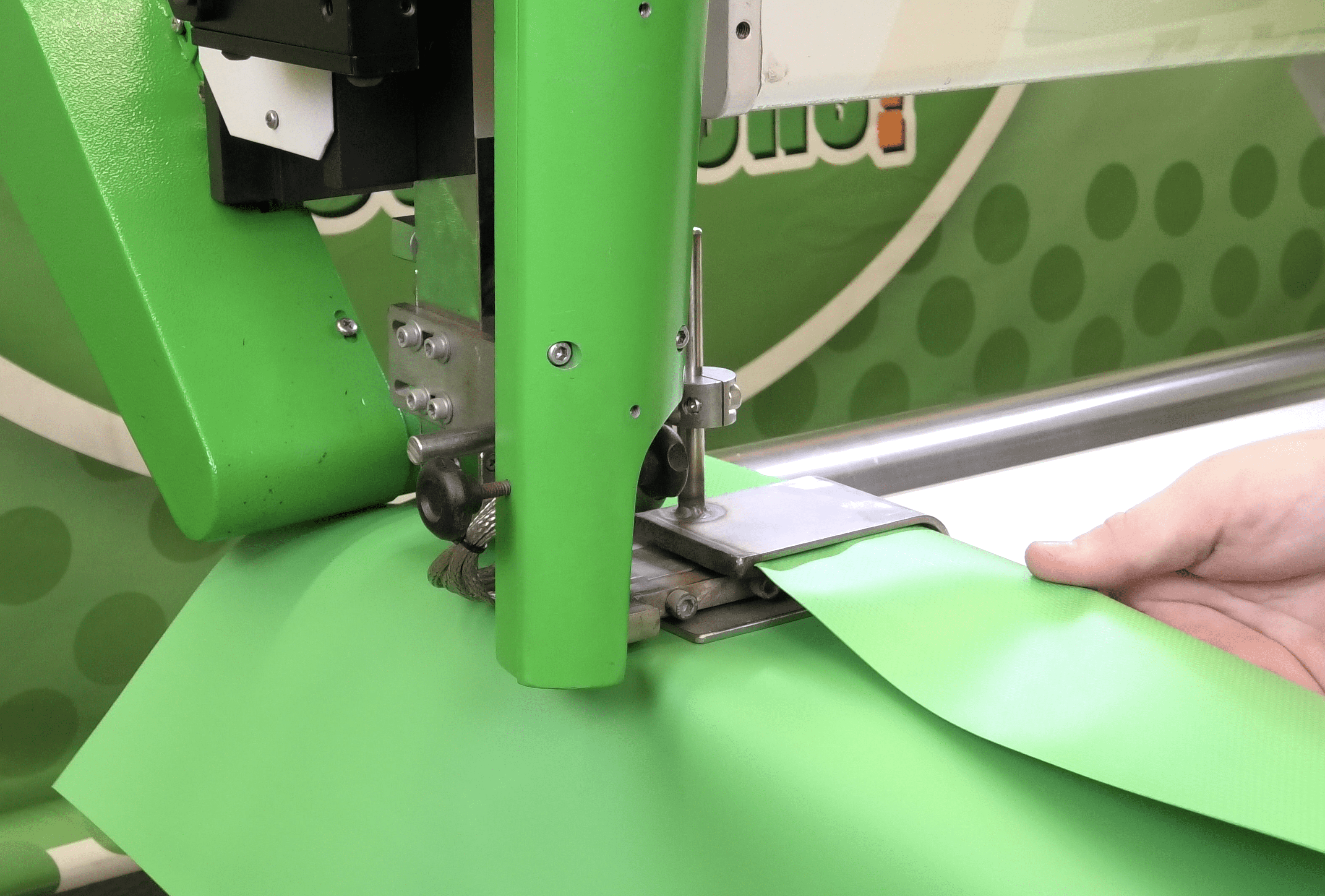
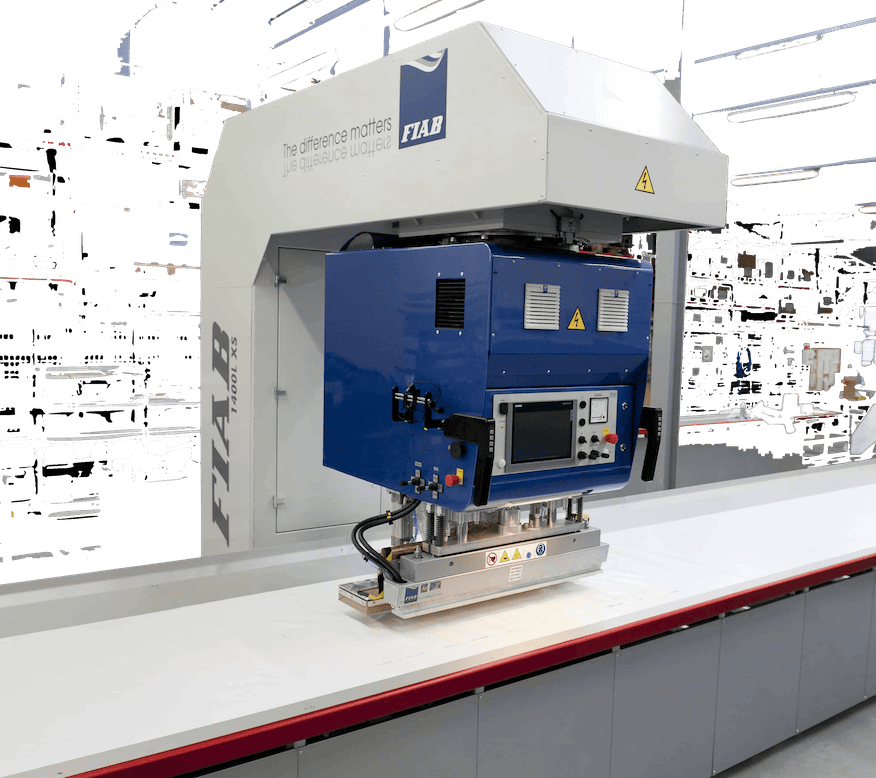
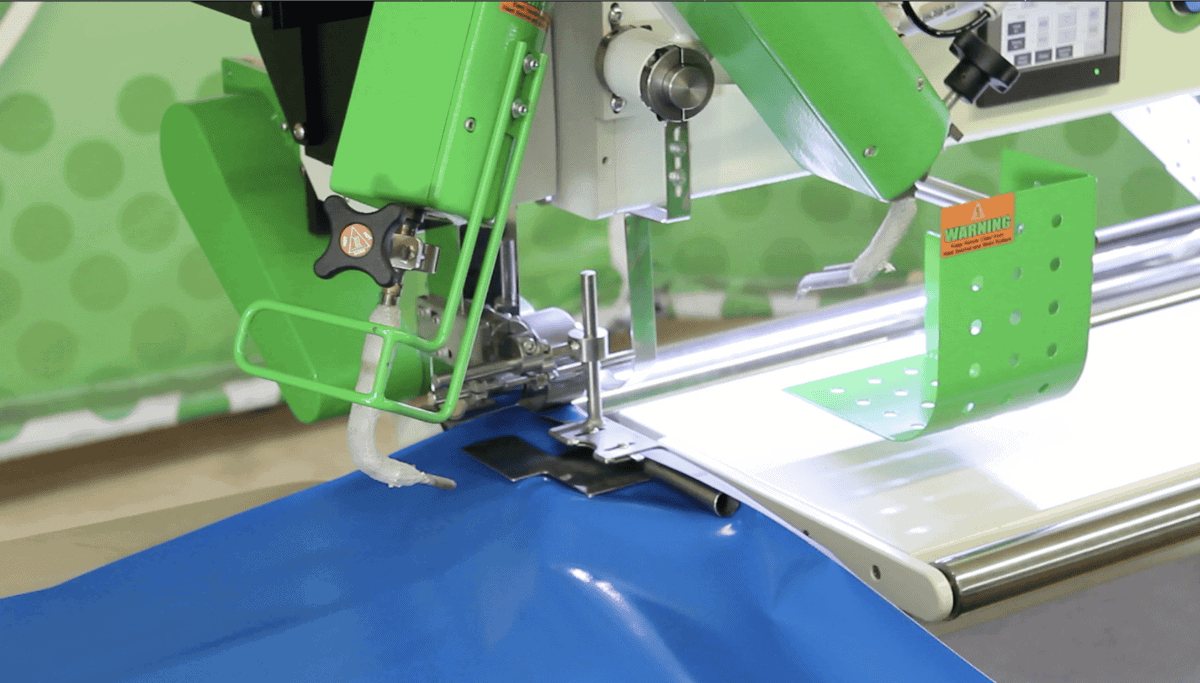
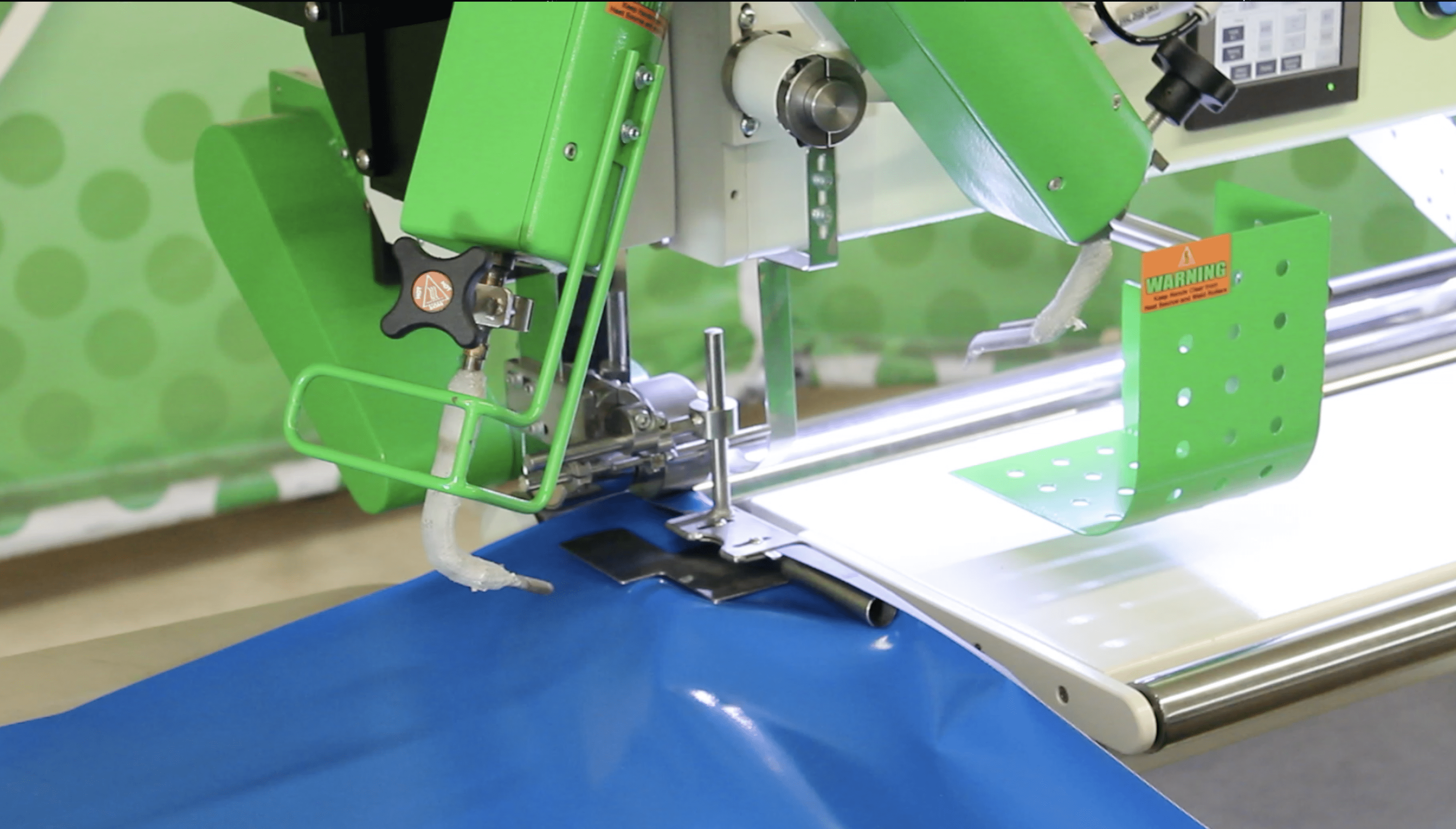
The ultimate success of PVC welding, lies in the details of its execution. The method of welding selected, the precise control over the welding parameters, and the compatibility of the welding method with the specific application or product design, all play a role in the final outcome. Here we’ll focus on the different types of PVC welding machines and the three primary PVC welding methods – Hot Air Welding, Hot Wedge Welding, and High Frequency Welding.
The Different Types of PVC Welding Machines
The world of PVC welding is replete with different types of machines, each designed for specific applications and optimized for unique product requirements. Understanding these machines is vital as they have a direct impact on the efficiency of the production process and the quality of the final product.
- Hot Air Welding Machine
These machines use heated air or gas to melt the contact points between materials, which then merge under pressure to form a strong bond. Hot air welding machines are typically leveraged for their versatility and are capable of handling a variety of product designs and materials. - Hot Wedge Welding Machines
Hot wedge welders use a heated wedge to apply heat at the seam interfaces. The heated wedge is driven between the two pieces of PVC, melting them before a pair of pressure rollers apply force, sealing the seam. These machines are often chosen for their precision, making them an excellent fit for applications where high accuracy is required. - High-Frequency Welding Machines:These utilize radio frequency energy to cause molecular agitation in the PVC. This agitation generates heat, which melts the materials at the seam. Once cooled, the seam forms a homogenous bond. High frequency welding machines are known for their speed and efficiency, which makes them particularly suitable for high-volume manufacturing environments.
The choice of a welding machine depends heavily on the specific requirements of the product being manufactured. For instance, if you are producing items with complex shapes or where the aesthetic appeal of the seam is a high priority, hot air welding machines might be the best fit. On the other hand, if you need fast-paced production without sacrificing seam quality, high-frequency welding could be the way to go.
A Deep Dive Into Welding Methods
Now that we covered the machines, let’s delve deeper into each of these three welding methods, exploring their advantages, limitations, and the types of products they are best suited for. This knowledge will empower you to make informed decisions when it comes to your manufacturing process, ultimately allowing you to create higher quality, more robust products.
Hot Air Welding
Hot Air Welding, as the name indicates, operates on the principle of applying heat to create a weld. A hot air welder uses a nozzle to blow hot air onto the PVC material, causing it to soften and melt. Once in this malleable state, the pieces of PVC are pressed together, forming a permanent bond when cooled.
One of the primary advantages of this method is the ability to create a very consistent weld, enhancing the product’s overall strength and durability. It is also highly versatile, and able to handle various shapes and sizes with relative ease. Whether you’re manufacturing flexible water tanks or inflatable boats, hot air welding offers the precision and strength necessary for diverse applications.
However, hot air welding does require careful temperature control to prevent overheating or under-heating, which can negatively impact the weld quality. But, with a skilled operator and the right settings, these potential limitations can be mitigated, yielding consistently high-quality results.
Hot Wedge Welding
Hot Wedge Welding uses a slightly different approach to the application of heat. A heated metal wedge is driven between the two pieces of PVC material, causing them to soften and melt. Following this, pressure is applied, typically through a pair of rollers, to merge the softened materials together. Once cooled, a firm and durable seam is formed.
This method offers the advantage of speed and consistency. The hot wedge can maintain a steady temperature, ensuring that the heat applied is uniform across the welding area. This process leads to a robust and permanent bond, ideal for applications that require durable, high-quality seams.
However, hot wedge welding may be less adaptable to complex or irregular shapes compared to hot air welding. Despite this limitation, for straightforward, linear welds, this method proves to be incredibly efficient and reliable.
High-Frequency Welding
High-frequency welding, sometimes referred to as radio frequency welding, uses radio waves to create heat and fuse PVC materials. The materials are placed between two metal plates, and a high-frequency electric field is applied. This process leads to molecular agitation within the PVC, generating heat and causing the material to melt and fuse together, creating a strong and durable seam.
The highlight of high-frequency welding is its speed welding capability. It is remarkably faster than hot air and wedge welding, making it an excellent choice for high-volume production runs. Additionally, the nature of the process results in a neat and tidy weld, enhancing the aesthetic appeal of the product.
However, it’s critical to note that high-frequency welding can only be used with certain materials that have specific dielectric properties, such as PVC. Where applicable though, it’s a powerful welding method that combines speed, consistency, and quality.
PVC welding for products that win in the test of time
In the end, PVC welding’s pivotal role in ensuring the durability and robustness of thermoplastic products across various industries cannot be underestimated. The waterproof nature of PVC, especially crucial in marine applications, is only as reliable as the seam bond created through welding. With the right method and precise controls, manufacturers can leverage PVC welding to create products that are not only functionally superior but also able to withstand the test of time.
Find the perfect welding fit with Erez Thermoplastics
As you navigate through the welding techniques and explore the one that’s for your production line, remember that every detail counts. From the type of welding to the machine used, all these aspects ultimately contribute to the quality of your final product.
Erez Thermoplastics is here to assist you on this journey. With our expertise in producing high-quality coated thermoplastic materials and deep understanding of PVC welding, we can guide you towards the optimal solution, ensuring that your products stand out in both quality and resilience.
Share this Post