Image courtesy of Miller Weldmaster
Hot Wedge (HW) Welding
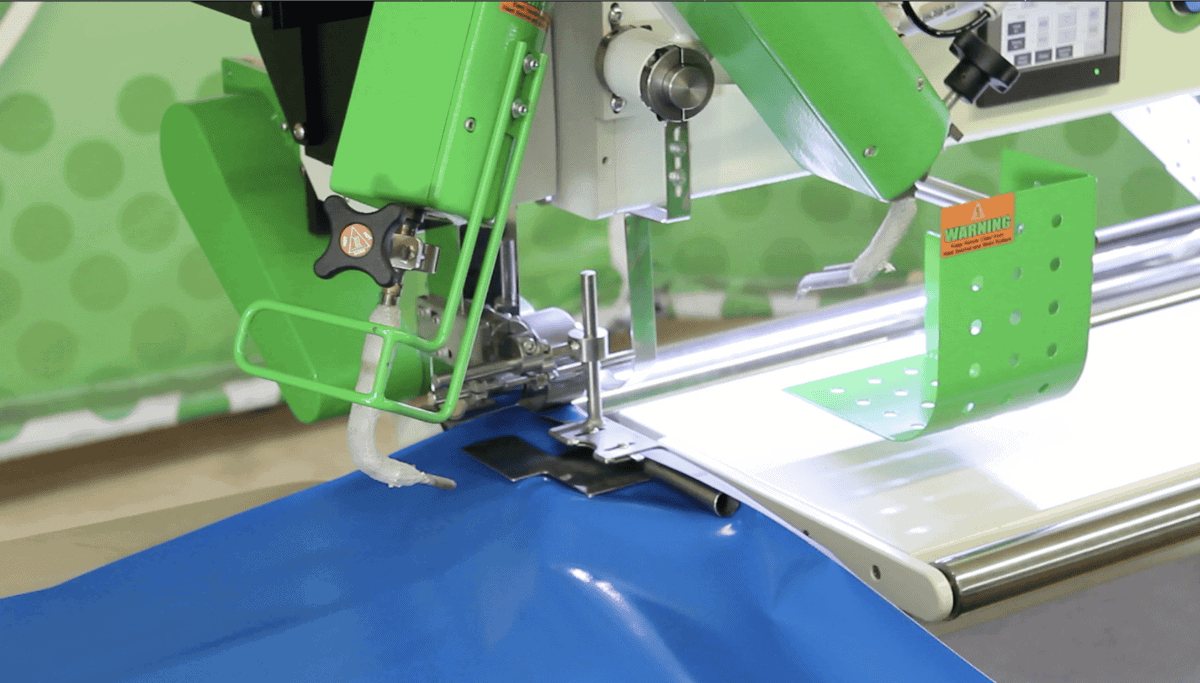
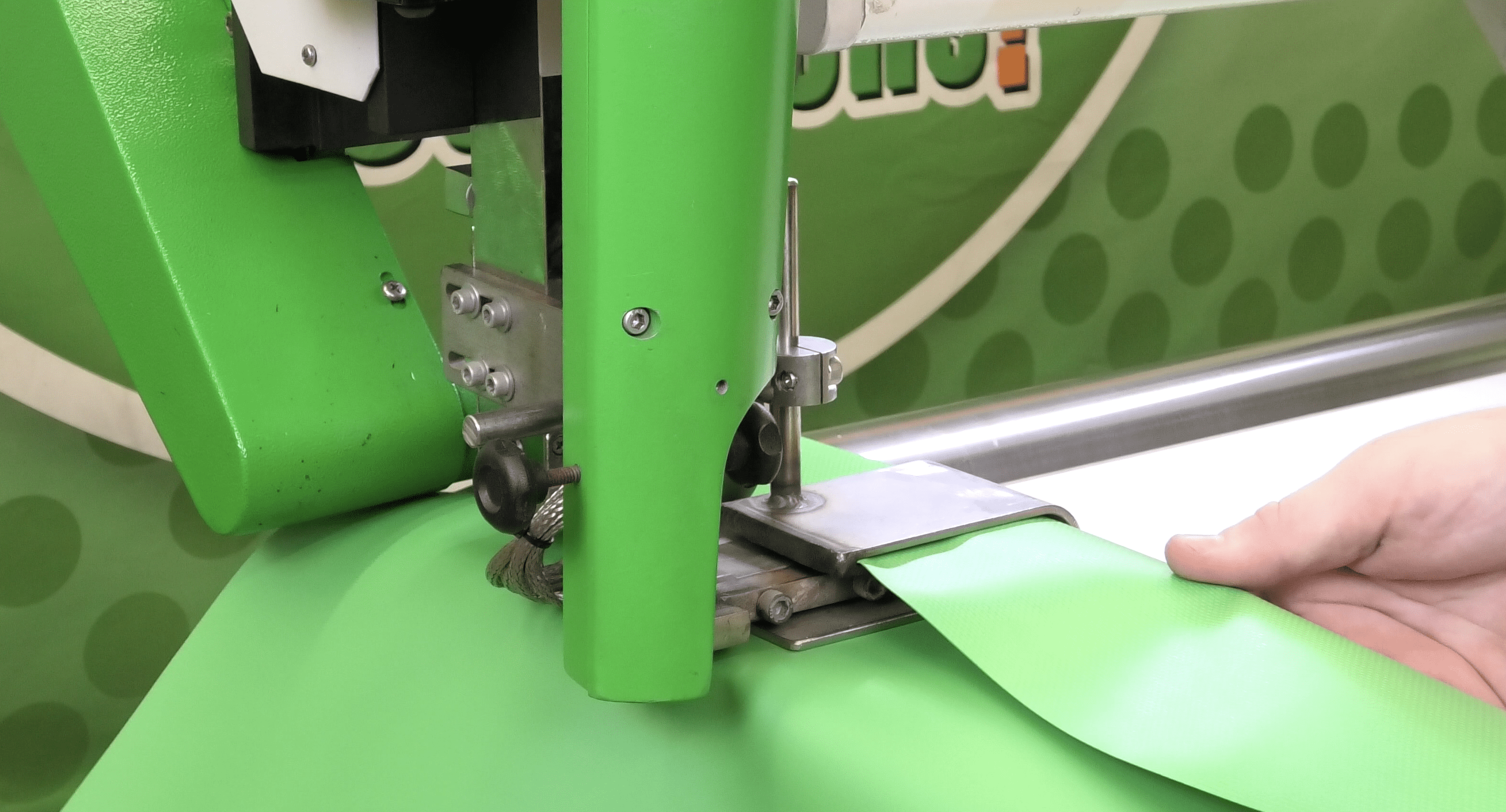
Hot wedge welding, also known as bar welding, uses a heated metal wedge to provide the required heat for melting the thermoplastics. The wedge is precisely positioned at the weld point as two sheets of fabric or film are pulled across the heated wedge. The material is moved across the wedge from above and below. The temperature of the wedge is highly controlled and can range from 370C to 493C (700F to 920F).
The weld is then subject to pressure from pinch rollers, or sometimes the pressure is applied by the welder himself, to form a smooth-seamed weld. Because pinch rollers are usually part of the welding machine, material can be welded without a tracking table. This ability makes HW welding ideal for portable apparatuses that are particularly useful in field applications where soft or uneven welding surfaces exist.
HW machines do not have high-frequency generators like high frequency welders or fans creating high-speed air flow like hot air welders. So, they are silent and nearly smokeless, creating a quiet, safe work environment.
Applications
HW welders can be set up to create multiple seams simultaneously and can perform many types of welds, including curved work. However, this method excels on straight seams and can be one of the fastest weld methods available. Depending on the application, weld times can range from 0.5 to 42 m/min.
HW welding is the preferred method when more than two layers need to be welded or when welding thermoplastic films with a thickness from 0.2 – 2mm (but usually less than 0.5mm) where air flow from hot-air welding can cause the material to flutter thereby affecting weld quality. It is also especially suited for PVC parts and TPU– and PVC-coated materials.
HW is often used in the manufacture of smaller tents, temporary inflatable structures, and to apply tape onto sewn seams. It is also used in flexible storage tanks, geomembrane works, tunneling, and roofing.
Geothermal Membranes
Portability, flexibility, and speed make HW welding the technique of choice for welding large-area geothermal membranes that must be field assembled. Geothermal membranes are frequently thick HDPE-coated industrial materials that are dual-track welded. Handheld apparatuses equipped with drive systems are used to ensure consistent welding speeds. The dual track method produces two parallel seams with a channel between them. The channel is used to blow air through to test for seam integrity.
Nonwoven geotextiles will only be tacked when HW welding is used. So, other welding methods should be used for more permanent seams with these materials. Like hot air welding, HW welding produces an open-ended seam that must be closed using another weld method.
EREZ Can Help
HW welding is not extensively used on materials that Erez manufactures, but it is still an important and common method for welding coated textiles. See our Ultimate Welding Guide for Coated Technical Textiles to learn more about HW techniques, as well as guidance on other welding types and techniques for every application.
Share this Post